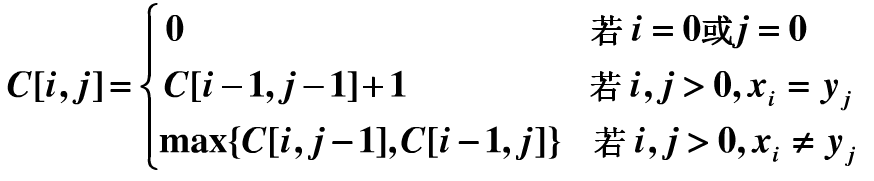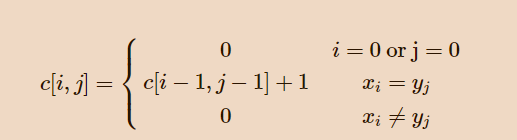import time
def cal_time(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
t1 = time.perf_counter()
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
t2 = time.perf_counter()
print("%s running time: %s sec." % (func.__name__, t2 - t1))
return result
return wrapper
# 动态规划求最长公共子序列:其实这不符合题意,因为是不讲究顺序的
def longestCommonSubsequence(s1: str, s2: str):
L1, L2 = len(s1), len(s2)
dp = []
for i in range(L1 + 1):
dp.append([0 for _ in range(L2 + 1)])
for i in range(L1):
for j in range(L2):
if s1[i] == s2[j]:
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j] + 1
else:
if dp[i + 1][j] > dp[i][j + 1]: # 水平
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i + 1][j]
else: # 竖直
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j + 1]
i, j = L1, L2
res = [0] * L1
while i > 0 and j > 0 and dp[i][j] > 0:
if dp[i][j] == dp[i][j - 1]:
j -= 1
elif dp[i][j] == dp[i - 1][j]:
i -= 1
elif dp[i][j] == (dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1):
res[i - 1] = 1
i -= 1
j -= 1
for i in range(len(res)):
if res[i] == 1:
print("<" + s1[i] + ">", end='')
else:
print(s1[i], end='')
# 动态规划求最长公共子串:按照顺序的
@cal_time
def longestCommonString(s1: str, s2: str):
L1, L2 = len(s1), len(s2)
dp = []
for i in range(L1 + 1):
dp.append([0 for _ in range(L2 + 1)])
x, y, maxValue = -1, -1, -1
for i in range(L1):
for j in range(L2):
if s1[i] == s2[j]: # 仅当相等才会在之前基础上增加,否则为0
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j] + 1
if dp[i + 1][j + 1] > maxValue:
maxValue = dp[i][j]
x, y = i + 1, j + 1
else:
continue
i, j = x, y
res = [0] * L1
startX = i
endX = i - 1
while i > 0 and j > 0 and dp[i][j] > 0:
res[i - 1] = 1
startX = i - 1
i -= 1
j -= 1
return s1[startX:endX + 1]
# 双指针求最长公共子串:按照顺序的,时间效率上比上一个方法快
@cal_time
def longestCommonString2(s1: str, s2: str):
maxLen = -1
resString = ''
sLen1, sLen2 = len(s1), len(s2)
for i in range(sLen1):
for j in range(sLen2):
x1 = i
x2 = j
if s1[i] != s2[j]:
continue
else:
while x1 < sLen1 and x2 < sLen2: # 判断有相等,继续扩充字符串
if s1[x1] == s2[x2]:
x1 += 1
x2 += 1
else:
break
curLen = x2 - j
if maxLen < curLen:
maxLen = curLen
resString = s2[j:x2]
return resString
# 使用3个字符串
def mainProcess(s1: str, s2: str, s3: str):
"""
# 方法1:
tmpString = longestCommonString(s1, s2)
resultString = longestCommonString(tmpString, s3)
print(resultString)
"""
# 方法2:
tmpString = longestCommonString2(s1, s2)
resultString = longestCommonString2(tmpString, s3)
returnString = ''
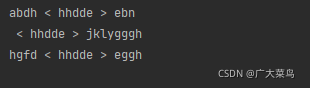
returnString += s1.replace(resultString, " < " + resultString + " > ") + '\n'
returnString += s2.replace(resultString, " < " + resultString + " > ") + '\n'
returnString += s3.replace(resultString, " < " + resultString + " > ")
return returnString
def readFile(filename):
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
return f.read()
def writeFile(filename, string: str):
with open(filename, 'w') as f:
f.write(string)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# fileroot = r'1/{}.txt'
# s1 = readFile(fileroot.format(1))
# s2 = readFile(fileroot.format(2))
# s3 = readFile(fileroot.format(3))
s1 = "abdhhhddeebn"
s2 = "hhddejklygggh"
s3 = "hgfdhhddeeggh"
string = mainProcess(s1, s2, s3)
print(string)
# writeFile(fileroot.format(4), string)
总结:最大子串是连续的部分,最大子序列是可以不连续的;
? ? ? ????????? 用动态规划,在这里不如双指针法
补充:考虑到如果文件内有多个公共子串,岂不是有多个公共子串(可能都是最长,或者相差不多),于是修改下,不为之前的使用最长公共子串,而是不交界的公共子串
效果:
import re
# 考虑到公共子串有可能为其他的子串的子串,在替换的时候,需要优先把长的串处理掉,避免异义
# 暂时没有啥好的想法,使用了正则表达式的替换+字符串格式化的方法
def myRe(strList: list, repLst: list):
repLst = sorted(repLst, key=lambda x: len(x), reverse=True) # 长的优先
resList = []
for string in strList:
tmpList = list()
index = 0
for i in range(len(repLst)):
rep = repLst[i]
if rep in string:
string = re.sub(rep, '{0[%d]}' % index, string)
tmpList.append('<%s>' % rep)
index += 1
string = string.format(tmpList)
resList.append(string)
return '\n'.join(resList)
def allCommonString(s1: str, s2: str):
L1, L2 = len(s1), len(s2)
dp = []
for i in range(L1 + 1):
dp.append([0 for _ in range(L2 + 1)])
for i in range(L1):
for j in range(L2):
if s1[i] == s2[j]: # 仅当相等才会在之前基础上增加,否则为0
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j] + 1
else:
continue
commonStrings = []
for x in range(1, L1 + 1):
for y in range(1, L2 + 1):
if dp[x][y] >= 2:
if x < L1 and y < L2 and dp[x + 1][y + 1] > 0:
continue
else:
i, j = x, y
startX = i
endX = i - 1
while i > 0 and j > 0 and dp[i][j] > 0:
startX = i - 1
i -= 1
j -= 1
commonStrings.append(s1[startX:endX + 1])
return commonStrings
def allCommonString2(s1: str, s2: str):
sLen1, sLen2 = len(s1), len(s2)
commonStrings = []
for i in range(sLen1):
for j in range(sLen2):
x1 = i
x2 = j
if s1[i] != s2[j]: # 比较时第一个字符不等
continue
else:
while x1 < sLen1 and x2 < sLen2: # 判断有相等,继续扩充字符串
if s1[x1] == s2[x2]:
x1 += 1
x2 += 1
else:
curLen = x2 - j
tmpStr = s2[j:x2]
if curLen > 2:
commonStrings.append(tmpStr)
break
if s1[x1 - 1] == s2[x2 - 1]:
curLen = x2 - j
tmpStr = s2[j:x2]
if curLen >= 2:
commonStrings.append(tmpStr)
return commonStrings
def mainProcess(s1: str, s2: str, s3: str) -> str:
commonStrings = allCommonString2(s1, s2)
commonStrings = list(set(commonStrings))
# 获取共同的交集:方法1:
# commonStrings2 = allCommonString(s1, s3)
# print(commonStrings2)
# sameStrings = list(set(commonStrings1)&set(commonStrings2))
# print(sameStrings)
# 获取共同交集:方法2:
i = 0
while 0 <= i < len(commonStrings):
if commonStrings[i] not in s3:
commonStrings.pop(i)
i -= 1
i += 1
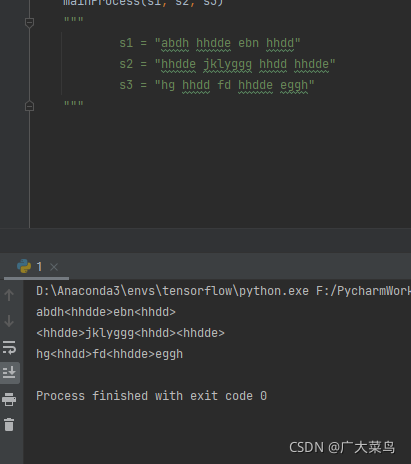
res = myRe([s1, s2, s3], commonStrings)
print(res)
return res
def readFile(filename):
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
return f.read()
def writeFile(filename, string: str):
with open(filename, 'w') as f:
f.write(string)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# fileroot = r'1/{}.txt'
# s1 = readFile(fileroot.format(1))
# s2 = readFile(fileroot.format(2))
# s3 = readFile(fileroot.format(3))
s1 = "abdhhhddeebnhhdd"
s2 = "hhddejklyggghhddhhdde"
s3 = "hghhddfdhhddeeggh"
mainProcess(s1, s2, s3)
"""
s1 = "abdh hhdde ebn hhdd"
s2 = "hhdde jklyggg hhdd hhdde"
s3 = "hg hhdd fd hhdde eggh"
"""
?
cs