def swap(a, p, i):
a[p], a[i] = a[i], a[p]
return a
#取第一个数,剩下的做排序,边界条件是开始索引p==终止索引q
def main(a, p, q):
res = []
def permute(a, p, q):
if p == q:
res.append(a.copy())
print('res:', res)
else:
for i in range(p, q, 1):
swap(a, p, i)
permute(a, p+1, q)
print('a:', a.copy())
swap(a, p, i)#a还原成原顺序,比如2开头的结束了是2 1 3 需要还原成1 2 3 在吧3放在开头在排序
print('==a:', a.copy())
permute(a, p, q)
print('==res:', res)
#
# a = [1]
# a = [1, 2]
a=[1, 2, 3]
main(a, 0, len(a))
class Solution:
def permute(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
def backtrack(first=0):
# 所有数都填完了
if first == n:
res.append(nums.copy())
for i in range(first, n):
# 动态维护数组
nums[first], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[first]
# 继续递归填下一个数
backtrack(first + 1)
# 撤销操作
nums[first], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[first]
n = len(nums)
res = []
backtrack()
return res
a = [1, 2, 3]
sol = Solution()
res = sol.permute(a)
print('===res:', res)
4.递归实现快速幂
问题:求 a 的 b 次方对 p 取模的值

#a^b%p
def a_b_p(a,b,p):
if b == 0:
return 1
elif b%2 == 1:#b是奇数
return a*a_b_p(a, b-1, p)%p
else:#b是偶数
temp = a_b_p(a, b//2, p)
return (temp*temp)%p
res = a_b_p(3,3,4)
print('==res:', res)

5.递归实现汉罗塔
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
//a--from b--temp c--to
void hano(int n, char a, char b, char c);
int main(){
hano(3, 'a', 'b', 'c');
return 0;
}
//a--from b--temp c--to
void hano(int n,char a, char b, char c){
if(n==1){
cout<<a<<"-->"<<c<<endl;
}
else{
hano(n-1, a, c, b);//c为temp,a上面的n-1给b
hano(1, a, b, c);//b为temp,a上面的1给c
hano(n-1, b, a, c);//a为temp,b上面的n-1给c
}
}

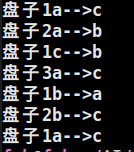
加上盘子序号:
盘子从上到底是1到n
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
//a--from b--temp c--to
void hano(int top, int n, char a, char b, char c);
int main(){
hano(1, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c');
return 0;
}
//a--from b--temp c--to
void hano(int top, int n,char a, char b, char c){
if(n==1){
cout<<"盘子"<<top<<a<<"-->"<<c<<endl;
}
else{
hano(top, n-1, a, c, b);//c为temp,a上面的n-1给b
hano(top + n - 1, 1, a, b, c);//b为temp,a上面的1给c
hano(top, n-1, b, a, c);//a为temp,b上面的n-1给c
}
}
cs







