网上查了很多资料,发现主要是使用邻接表来实现图,并进行遍历的。而采用邻接矩阵的就非常少。
不得已,就只有闭门造车,埋头苦修。小有成果,供后来学习者研究。
- 通过二维数组建立无向图
- 通过二维数组建立有向图
- 通过边建立有向图
- 为方便查看,通过NetworkX显示图。
不想看的可以直接下载:python 邻接矩阵三种方法实现有向图、无向图,并绘图显示
不废话。上代码
首先图类
class Graph_Matrix:
"""
Adjacency Matrix
"""
def __init__(self, vertices=[], matrix=[]):
"""
:param vertices:a dict with vertex id and index of matrix , such as {vertex:index}
:param matrix: a matrix
"""
self.matrix = matrix
self.edges_dict = {}
self.edges_array = []
self.vertices = vertices
self.num_edges = 0
if len(matrix) > 0:
if len(vertices) != len(matrix):
raise IndexError
self.edges = self.getAllEdges()
self.num_edges = len(self.edges)
elif len(vertices) > 0:
self.matrix = [[0 for col in range(len(vertices))] for row in range(len(vertices))]
self.num_vertices = len(self.matrix)
def isOutRange(self, x):
try:
if x >= self.num_vertices or x <= 0:
raise IndexError
except IndexError:
print("节点下标出界")
def isEmpty(self):
if self.num_vertices == 0:
self.num_vertices = len(self.matrix)
return self.num_vertices == 0
def add_vertex(self, key):
if key not in self.vertices:
self.vertices[key] = len(self.vertices) + 1
for i in range(self.getVerticesNumbers()):
self.matrix[i].append(0)
self.num_vertices += 1
nRow = [0] * self.num_vertices
self.matrix.append(nRow)
def getVertex(self, key):
pass
def add_edges_from_list(self, edges_list):
for i in range(len(edges_list)):
self.add_edge(edges_list[i][0], edges_list[i][1], edges_list[i][2], )
def add_edge(self, tail, head, cost=0):
if tail not in self.vertices:
self.add_vertex(tail)
if head not in self.vertices:
self.add_vertex(head)
self.matrix[self.vertices.index(tail)][self.vertices.index(head)] = cost
self.edges_dict[(tail, head)] = cost
self.edges_array.append((tail, head, cost))
self.num_edges = len(self.edges_dict)
def getEdges(self, V):
pass
def getVerticesNumbers(self):
if self.num_vertices == 0:
self.num_vertices = len(self.matrix)
return self.num_vertices
def getAllVertices(self):
return self.vertices
def getAllEdges(self):
for i in range(len(self.matrix)):
for j in range(len(self.matrix)):
if 0 < self.matrix[i][j] < float('inf'):
self.edges_dict[self.vertices[i], self.vertices[j]] = self.matrix[i][j]
self.edges_array.append([self.vertices[i], self.vertices[j], self.matrix[i][j]])
return self.edges_array
def __repr__(self):
return str(''.join(str(i) for i in self.matrix))
def to_do_vertex(self, i):
print('vertex: %s' % (self.vertices[i]))
def to_do_edge(self, w, k):
print('edge tail: %s, edge head: %s, weight: %s' % (self.vertices[w], self.vertices[k], str(self.matrix[w][k])))
第一种方法,二维数组生成图
def create_undirected_matrix(my_graph):
nodes = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h']
matrix = [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0]]
my_graph = Graph_Matrix(nodes, matrix)
print(my_graph)
return my_graph
第二种方法,二维数组生成有向图
def create_directed_matrix(my_graph):
nodes = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h']
inf = float('inf')
matrix = [[0, 2, 1, 3, 9, 4, inf, inf],
[inf, 0, 4, inf, 3, inf, inf, inf],
[inf, inf, 0, 8, inf, inf, inf, inf],
[inf, inf, inf, 0, 7, inf, inf, inf],
[inf, inf, inf, inf, 0, 5, inf, inf],
[inf, inf, 2, inf, inf, 0, 2, 2],
[inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, 1, 0, 6],
[inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, 9, 8, 0]]
my_graph = Graph_Matrix(nodes, matrix)
print(my_graph)
return my_graph
第三种方法,用边生成有向图
def create_directed_graph_from_edges(my_graph):
nodes = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G']
edge_list = [('A', 'F', 9), ('A', 'B', 10), ('A', 'G', 15), ('B', 'F', 2),
('G', 'F', 3), ('G', 'E', 12), ('G', 'C', 10), ('C', 'E', 1),
('E', 'D', 7)]
my_graph = Graph_Matrix(nodes)
my_graph.add_edges_from_list(edge_list)
print(my_graph)
return my_graph
最后显示图像代码
1.显示无向图
def draw_undircted_graph(my_graph):
G = nx.Graph()
for node in my_graph.vertices:
G.add_node(str(node))
for edge in my_graph.edges:
G.add_edge(str(edge[0]), str(edge[1]))
print("nodes:", G.nodes())
print("edges:", G.edges())
print("number of edges:", G.number_of_edges())
nx.draw(G, with_labels=True)
plt.savefig("undirected_graph.png")
plt.show()
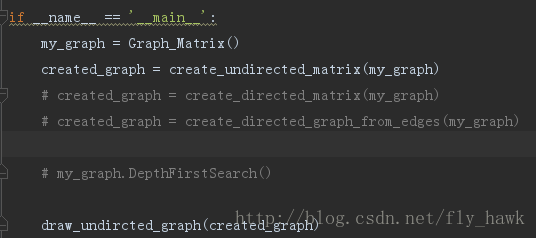
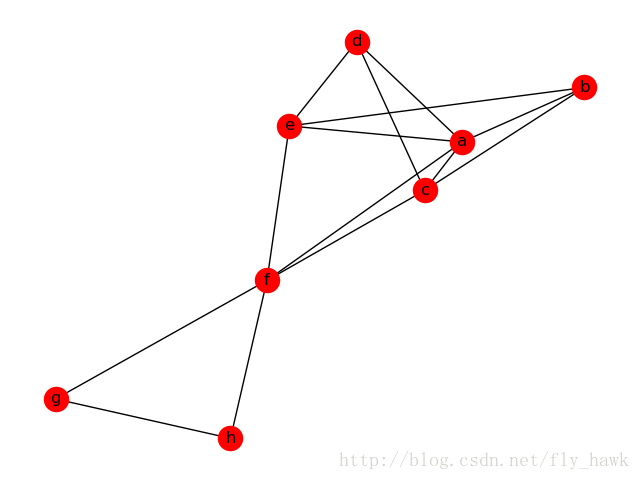
2.显示有向图,带权
def draw_directed_graph(my_graph):
G = nx.DiGraph()
for node in my_graph.vertices:
G.add_node(str(node))
G.add_weighted_edges_from(my_graph.edges_array)
print("nodes:", G.nodes())
print("edges:", G.edges())
print("number of edges:", G.number_of_edges())
nx.draw(G, with_labels=True)
plt.savefig("directed_graph.png")
plt.show()
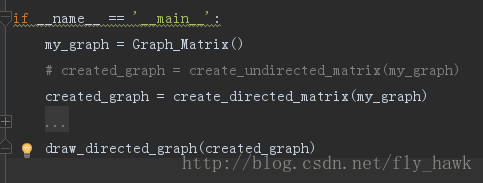
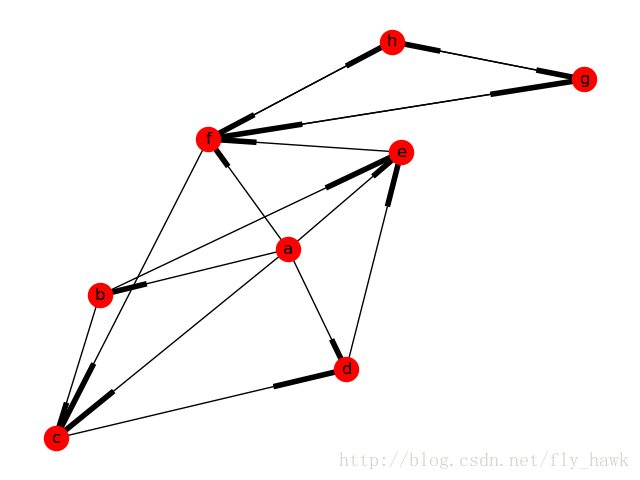
cs





