目录
- 一、CrawlSpider类介绍
- 二、案例:古诗文网全站数据爬取
- 2.1 爬虫文件
- 2.2 item文件
- 2.3 管道文件
- 2.4 配置文件
- 2.5 输出结果
一、CrawlSpider类介绍
1.1 引入
使用scrapy框架进行全站数据爬取可以基于Spider类,也可以使用接下来用到的CrawlSpider类。基于Spider类的全站数据爬取之前举过栗子,感兴趣的可以康康
scrapy基于CrawlSpider类的全站数据爬取
1.2 介绍和使用
1.2.1 介绍
CrawlSpider是Spider的一个子类,因此CrawlSpider除了继承Spider的特性和功能外,还有自己特有的功能,主要用到的是 LinkExtractor()和rules = (Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'Items/'), callback='parse_item', follow=True),)
LinkExtractor():链接提取器
LinkExtractor()接受response对象,并根据allow对应的正则表达式提取响应对象中的链接
link = LinkExtractor(
# Items只能是一个正则表达式,会提取当前页面中满足该"正则表达式"的url
allow=r'Items/'
)
rules = (Rule(link, callback='parse_item', follow=True),):规则解析器
按照指定规则从链接提取器中提取到的链接中解析网页数据
link:是一个LinkExtractor()对象,指定链接提取器
callback:回调函数,指定规则解析器(解析方法)解析数据
follow:是否将链接提取器继续作用到链接提取器提取出的链接网页中
import scrapy
# 导入相关的包
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule
class TextSpider(CrawlSpider):
name = 'text'
allowed_domains = ['www.xxx.com']
start_urls = ['http://www.xxx.com/']
# 链接提取器,从接受到的response对象中,根据item正则表达式提取页面中的链接
link = LinkExtractor(allow=r'Items/')
link2 = LinkExtractor(allow=r'Items/')
# 规则解析器,根据callback将链接提取器提取到的链接进行数据解析
# follow为true,则表示将链接提取器继续作用到链接提取器所提取到的链接页面中
# 故:在我们提取多页数据时,若第一页对应的网页中包含了第2,3,4,5页的链接,
# 当跳转到第5页时,第5页又包含了第6,7,8,9页的链接,
# 令follow=True,就可以持续作用,从而提取到所有页面的链接
rules = (Rule(link, callback='parse_item', follow=True),
Rule(link2,callback='parse_content',follow=False))
# 链接提取器link使用parse_item解析数据
def parse_item(self, response):
item = {}
yield item
# 链接提取器link2使用parse_content解析数据
def parse_content(self, response):
item = {}
yield item
1.2.2 使用
创建爬虫文件:除了创建爬虫文件不同外,创建项目和运行爬虫使用的命令和基于Spider类使用的命令相同
scrapy genspider crawl -t spiderName www.xxx.com
二、案例:古诗文网全站数据爬取
爬取古诗文网首页古诗的标题,以及每一首诗详情页古诗的标题和内容。
最后将从详情页提取到的古诗标题和内容进行持久化存储
2.1 爬虫文件
import scrapy
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule
from gushiPro.items import GushiproItem,ContentItem
class GushiSpider(CrawlSpider):
name = 'gushi'
#allowed_domains = ['www.xxx.com']
start_urls = ['https://www.gushiwen.org/']
# 链接提取器:只能使用正则表达式,提取当前页面的满足allow条件的链接
link = LinkExtractor(allow=r'/default_\d+\.aspx')
# 链接提取器,提取所有标题对应的详情页url
content_link = LinkExtractor(allow=r'cn/shiwenv_\w+\.aspx')
rules = (
# 规则解析器,需要解析所有的页面,所有follow=True
Rule(link, callback='parse_item', follow=True),
# 不需要写follow,因为我们只需要解析详情页中的数据,而不是详情页中的url
Rule(content_link, callback='content_item'),
)
# 解析当前页面的标题
def parse_item(self, response):
p_list = response.xpath('//div[@class="sons"]/div[1]/p[1]')
for p in p_list:
title = p.xpath('./a//text()').extract_first()
item = GushiproItem()
item['title'] = title
yield item
# 解析详情页面的标题和内容
def content_item(self,response):
# //div[@]/div[@class="cont"]/div[@class="contson"]
# 解析详情页面的内容
content = response.xpath('//div[@]/div[@class="cont"]/div[@class="contson"]//text()').extract()
content = "".join(content)
# # 解析详情页面的标题
title = response.xpath('//div[@]/div[@class="cont"]/h1/text()').extract_first()
# print("title:"+title+"\ncontent:"+content)
item = ContentItem()
item["content"] = content
item["title"] = title
# 将itme对象传给管道
yield item
2.2 item文件
import scrapy
# 不同的item类是独立的,他们可以创建不同的item对象
class GushiproItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
title = scrapy.Field()
class ContentItem(scrapy.Item):
title = scrapy.Field()
content = scrapy.Field()
2.3 管道文件
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
class GushiproPipeline:
def __init__(self):
self.fp = None
def open_spider(self,spider):
self.fp = open("gushi.txt",'w',encoding='utf-8')
print("开始爬虫")
def process_item(self, item, spider):
# 从详情页获取标题和内容,所以需要判断爬虫文件中传来的item是什么类的item
# item.__class__.__name__判断属于什么类型的item
if item.__class__.__name__ == "ContentItem":
content = "《"+item['title']+"》",item['content']
content = "".join(content)
print(content)
self.fp.write(content)
return item
def close_spider(self,spider):
self.fp.close()
print("结束爬虫")
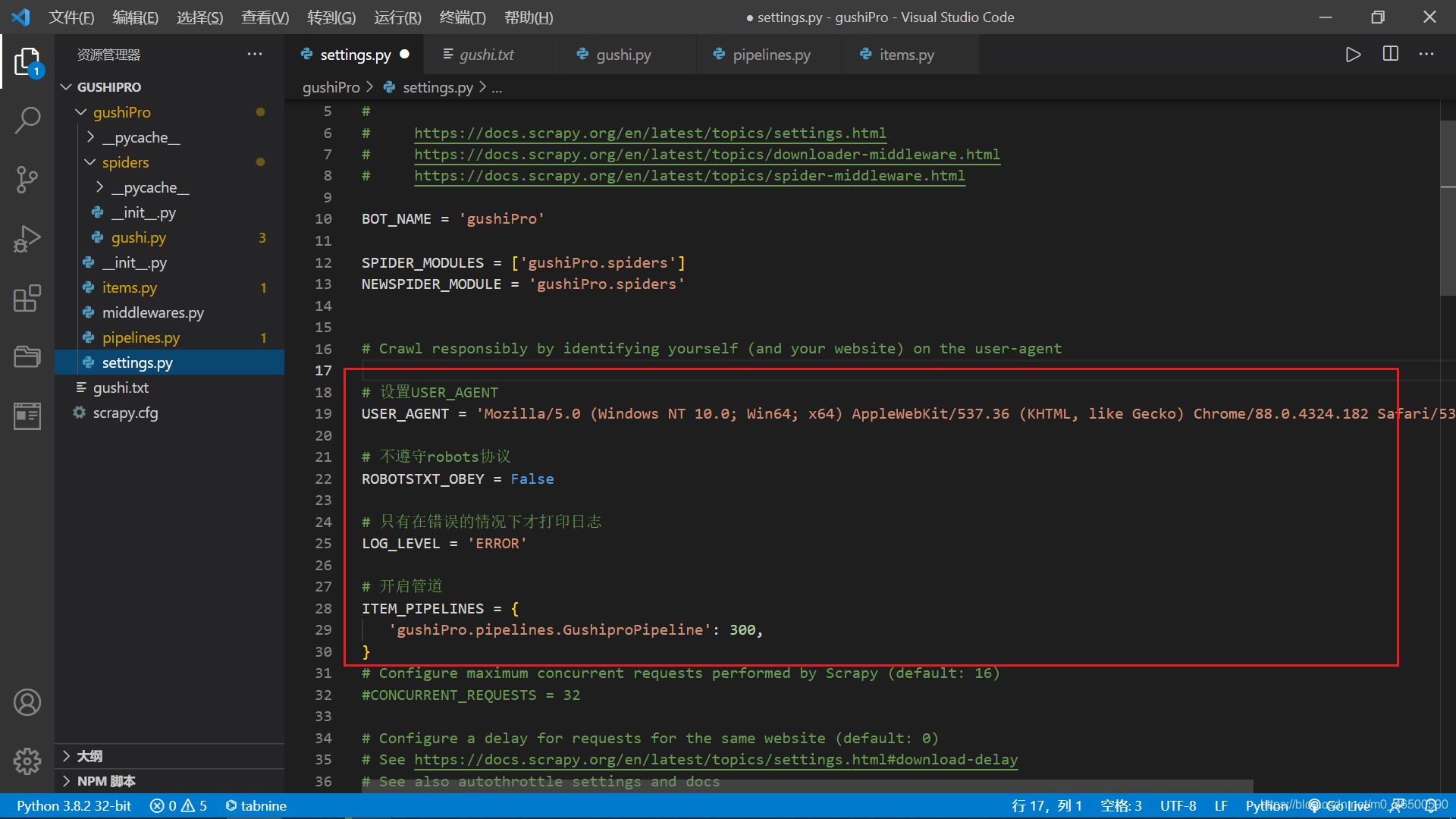
2.4 配置文件
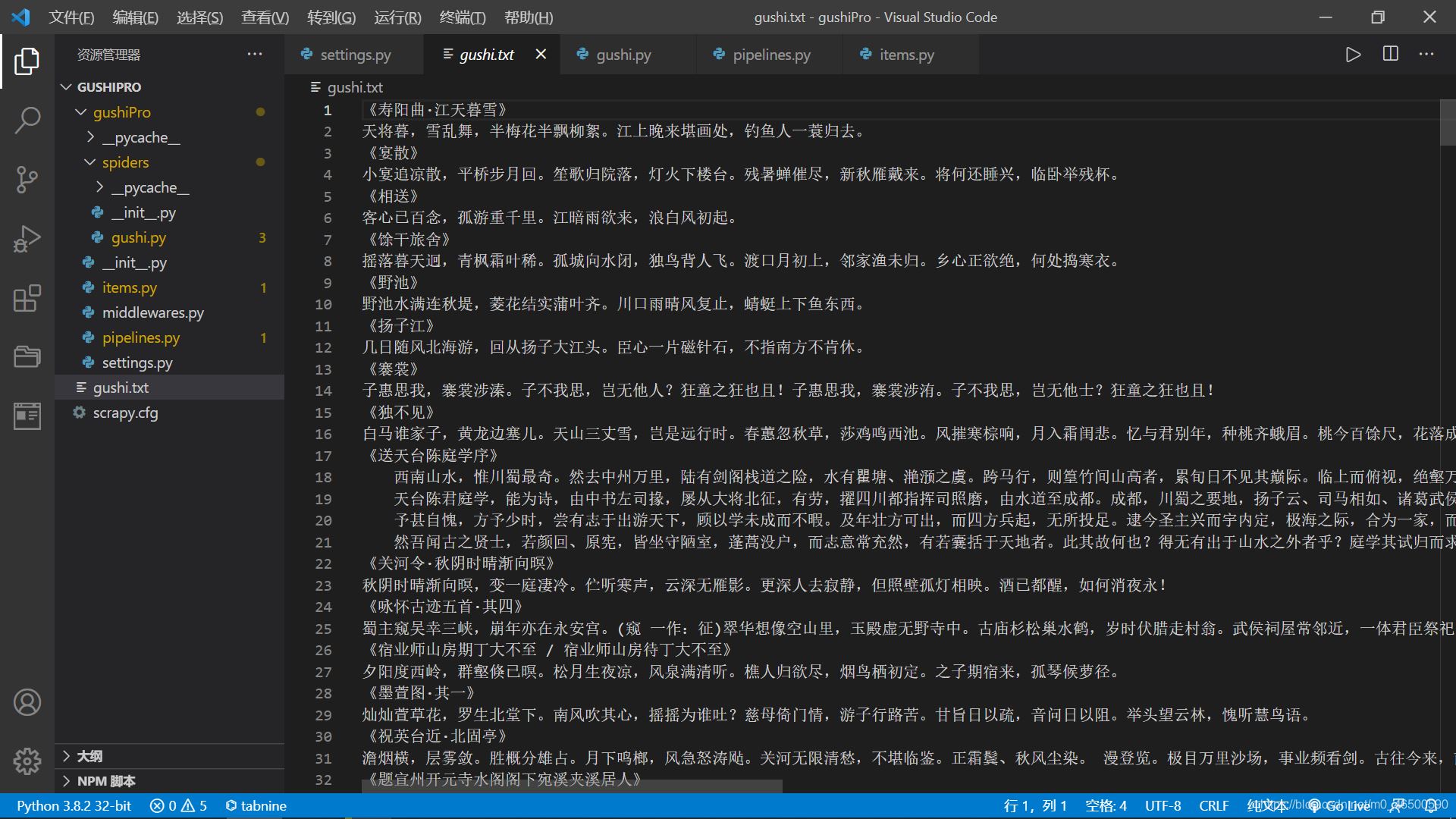
2.5 输出结果
jsjbwy



